The Four Stages of the OCD Cycle and How to Break Free

Do you find yourself in a seemingly never-ending cycle of intrusive thoughts and compulsive behaviors? If yes, then you might be experiencing an obsessive-compulsive disorder cycle. Obsessive-compulsive disorder most commonly known as OCD is an anxiety disorder that affects millions of people around the world.
Having OCD is like having an unwanted passenger in your mind, who never stops talking, and who’s constantly pushing you to do things you don’t want to do. It can be as annoying as meeting the aunties in your family who nag you every time you see them but can’t avoid them.
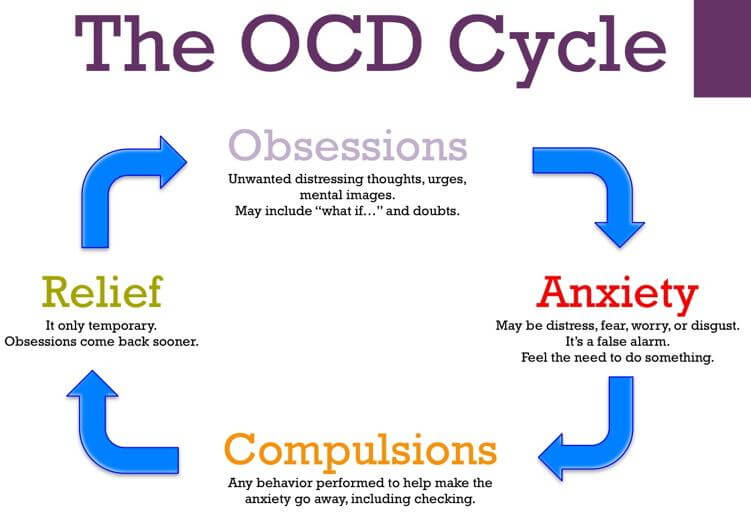
Even though obsessions and compulsions in OCD might be different, there is one experience that remains common – the OCD Cycle. This cycle consists of 4 stages – obsessive thoughts, anxiety, compulsive behavior, and temporary relief. Keep reading to know what is an OCD cycle, the 4 stages of the OCD cycle, and how you can break free of them.
What is an OCD Cycle?
An OCD cycle is like the hamster wheel of your mind, where intrusive or obsessive thoughts (obsessions) cause repetitive actions (compulsions) to relieve anxiety. Here’s an example; Someone with contamination OCD might compulsively wash their hands to feel safe, but the relief they get is only temporary. This cycle can overtake your life, trapping you in a loop of distress.
An OCD cycle can be triggered by various factors. Some believe that OCD can be genetic, while others believe that imbalances in the brain can trigger the condition. Stressful events in life, traumatic experiences, and even negative interactions in the past can trigger OCD or make it worse.
The 4 Stages in an OCD Cycle
There are four stages in an OCD cycle;
- Obsessions or Obsessive Thoughts
- Anxiety
- Compulsions or Compulsive Behaviors
- Temporary Relief
1. Obsessions or Obsessive Thoughts
The OCD cycle begins with intrusive thoughts or obsessive thoughts. These thoughts can be about your OCD type and trigger, for example; cleanliness, harming yourself or others, symmetry obsessions, forbidden thoughts, etc. These obsessions or distressing thoughts can cause intense anxiety and discomfort.
2. Anxiety
As your intrusive thoughts take hold, anxiety and distress skyrocket. While the theme of obsessions might vary depending on the type of OCD, anxiety remains a common thread. You may feel compelled to do something about your obsessive thoughts to alleviate the anxiety, leading to the next stage which is compulsions.
3. Compulsions or Compulsive Behaviors
To reduce the anxiety and distress you feel, you may resort to acting out on your thoughts aka performing compulsions. Compulsions are repetitive behaviors or acts that you engage in to relieve anxiety. For example; if you have a symmetry OCD and see a picture frame that is hung asymmetrically, then you may feel (and eventually act on) the urge to correct it. However, compulsions offer temporary relief. Which is the next stage of the OCD cycle.
4. Temporary Relief
After you perform the compulsion, there is a brief moment of reprieve. Your anxiety (from the second stage of the OCD cycle) decreases, but only temporarily. However, after some time, you may experience the obsessions once more, kick-starting the OCD cycle once more.
How to Break the OCD Cycle?
Breaking an OCD cycle is challenging but it is possible to break it. Here are some ways that can help you break the OCD cycle;
1. Become Self-Aware
The first thing you can do to break the OCD cycle is to recognize the obsessions and compulsions for what they are. When you recognize that these thoughts are a part of your OCD, then you’ll get closer to your recovery and breaking free of this OCD cycle.
2. Resist the Urge
Whenever your obsessions arise, resist the urge to engage in the compulsions. This can be challenging for you as it’ll make you feel more anxious, but resisting the urges to perform compulsions is an important step in reducing the power they hold over you.
3. Practice Calming Techniques
There are ways you can ground yourself when it becomes difficult to resist the urge to engage in compulsions. OCD calming techniques such as meditation, mindfulness, and other grounding techniques can help you be aware of the present moment and let thoughts, emotions, and sensations pass without paying any attention to them. This can reduce the anxiety you associate with obsessions.
4. Exposure Therapy
Psychotherapy approaches such as exposure therapy can help in breaking the OCD cycle as well. This therapy is an approach where you gradually face your fears and resist the compulsions. With time and under the supervision of a psychologist, you can learn to address anxiety and resist obsessions and compulsions.
5. Medications
In some severe cases, a psychiatrist may prescribe medications to help manage OCD symptoms. Please consult with a professional psychiatrist or your physician before taking any medications as some of the medications might have side effects that can worsen your OCD.
When to Seek Help?
If your OCD symptoms are affecting your everyday life and causing undue distress, then don’t hesitate to seek help from a professional. You don’t have to go through with this alone. Reach out to a mental health professional who can offer guidance, support, and treatment options best suited to your needs.
You can also consider joining online or offline OCD support groups or forums where you can find people with whom you can talk and share experiences. You can also learn how to overcome OCD symptoms and cope with the OCD cycle through others’ experiences.
Wrapping Up…
Understanding the four stages of the OCD cycle can be one of many steps toward breaking free from them. The stages of the OCD cycle; obsessions, anxiety, compulsions, and temporary relief, gain strength when you keep feeding them. It’s important to learn how to break the OCD cycle to live a fulfilling and stress-free life.
With psychotherapy approaches such as exposure therapy and self-help strategies such as being self-aware and practicing OCD calming techniques, you can let go of the cycle and reclaim control of your life.
So, take the first step today, seek help, and set your sights on the path to a happier life. You can do this!
Was this article helpful? Let me know what you think about the OCD cycle and the steps to break the OCD cycle in the comments box below.
Take Care!