Exploring The Differences Between Anorexia Nervosa And Bulimia Nervosa

Generally, there are various types of eating disorders but anorexia and bulimia nervosa are the common ones with similar symptoms but characterized by different behaviors. There are a lot of differences between anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa but due to some similarities, people often get confused between the two.
Well, not anymore! In this blog, I have enlisted some important differences between anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa that will help you distinguish between the two common types of eating disorders. So, let’s get started!
Also Read: Long Term Effects Of Bulimia Nervosa: Things You Should Keep In Mind
What is Anorexia Nervosa?
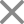
Anorexia nervosa is an eating disorder wherein people stop eating or eat less. The severity of symptoms of anorexia nervosa can be calculated by the BMI Index by measuring the height and weight of the individual. For example, when an individual’s BMI severely decreases, the severity of severe anorexia increases.
This happens because people want to get a slim body as a result they start eating less or stop eating at all. Not only does it impact the physical health of individuals, but it also severely impacts the mental health of individuals.
Due to its highest rate of mortality, this eating disorder is referred to as one of the most dangerous eating disorders. Talking about psychological reasons behind the development of anorexia nervosa, people mostly struggle with insecurities, negative self-image, body-shaming, low self-esteem, and more.
People struggling with anorexia nervosa mainly believe they are overweight or obese so they start eating less which slowly becomes an obsession, and they become anxious about gaining extra inches. People with anorexia nervosa often get involved in activities like calculating calories, weighing servings or portions, or measuring themselves compulsively.
What is Bulimia Nervosa?
Bulimia nervosa is also referred to as a binge eating disorder wherein people eat more than they should. Additionally, such people also show symptoms of purging such as using laxatives, vomiting forcefully, overexertion, and more. Basically, people struggling with bulimia nervosa eat more and then purge forcefully to prevent weight gain and other consequences. The major causes of bulimia nervosa often revolve around negative self-image, bad parenting, low self-esteem, scarred childhood, and more.
Due to fewer changes and more secretive purging, this disorder mostly goes underdiagnosed. However, it can go to an extreme level and can be really physically and mentally frightening. This eating disorder is likely to be more present in women as compared to men since women’s jobs are more based on bodily activities such as models, performers, influencers, dancers, and more.
Therefore, they are more likely to be criticized for their bodies and can develop anxiety which can turn into binge eating and purging excessively.
Differences Between Anorexia Nervosa and Bulimia Nervosa
Both eating disorders are caused by a common factor: eating and getting lean as possible! However, based on the different definitions, there can be other differences as well which can help distinguish between the two eating disorders easily! One of the effective ways to understand the differences between anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa is to understand the signs and symptoms of both. In this section, let us contrast anorexia and bulimia based on symptoms:
Symptoms of Anorexia Nervosa
Since anorexic symptoms are mostly rooted in a distorted self-image, which can also be caused by emotional trauma, underlying anxiety, or depression, some people start getting involved in extreme dieting or weight loss as a way to improve their social image. Clearly, this behavior can have emotional, physical, and mental symptoms such as:
Physical Symptoms of Anorexia Nervosa
- Blue lining across fingers
- Constipation
- Dehydration
- Fainting or dizziness
- Fatigue or weakness
- Improper menstruation or amenorrhea
- Incapability to tolerate cold
- Insomnia or changes in sleep pattern
- Irregular heartbeat or arrhythmia
- Presence of downy hair
- Thinning or extreme hair fall due to nutrient loss
- Weight loss
- Yellowish, pale, or dry skin
Behavioral Symptoms of Anorexia Nervosa
- Adaptation of unusual eating habits like cutting food into smaller pieces, or sorting the food out
- Constant meal skipping
- Extreme consumption of low-calorie foods
- Extreme body movements or exercising
- Lying about consuming food or nutrients
- Poor body image
- Trying to hide the curves by wearing baggy clothes
- Social withdrawal or avoiding social situations intentionally
Emotional Symptoms of Anorexia Nervosa
- Anxiety
- Agitation or irritation
- Depression
- Lack of self-esteem
- Poor body image
- Severe mood changes
- Social isolation
Symptoms of Bulimia Nervosa
Bulimia nervosa revolves around an unhealthy relationship with eating. People who struggle with bulimia nervosa are often seen in unhealthy or damaging behaviors related to binge eating and panicking about the extra calories they might consume during the episode. Such behavior can go to an extreme level. The most common symptom of bulimia nervosa is anxiety since people are involved in binge eating and purging compulsively.
Symptoms of bulimia nervosa can be emotional, physical, and behavioral. Below listed are some of the common symptoms of bulimia nervosa:
Physical Symptoms of Bulimia Nervosa
- Bloodshot eyes
- Cracked or chapped lips
- Extreme weight gain or weight loss in significant pounds such as 5 to 20 pounds in a week
- Sores, scars, or calluses on the knuckles due to extreme vomiting
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Sensitive mouth
Emotional Symptoms of Bulimia Nervosa
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Extreme mood changes, irritation, or agitation
- Lack of self-esteem
- Poor body image
- Social isolation or social withdrawal
Behavioral Symptoms of Bulimia Nervosa
- Avoiding high-calorie foods or restricting calories
- Extreme exercising
- Extreme worrying about physical appearance or weight
- Eating due to discomfort and not fulfilling nutrient loss
- Inability to eat in front of everyone
- Rushing to the bathroom right after eating
Final Comparison
Getting Help
If you think you or your loved one might be struggling with an eating disorder or one of these eating disorders, you must connect with a health provider in the first place. A physician might order some tests to make a diagnosis and rule out the presence of other health issues. In such situations, you can also connect with a mental health professional, a mental health professional is likely to make a diagnosis based on the Diagnostic and Statistical Mental Health Disorders 5th Edition (DSM_5).
To connect with an experienced and certified mental health professional through online platforms, refer to:

Great for a large network of licensed therapists
-
$60 to $90/week, billed every 4 weeks
-
Therapy via messaging, phone, or live video chat
-
Flexible cancellation at any time
20% off your first month

Great for CBT Based therapists
-
$40/week, billed every 4 weeks
-
Therapy via messaging, phone, or live video chat
-
Specialization for CBT based Therapy
20% off your first month

Best for Treatment Plants
-
$60 to $90/week, billed every 4 weeks
-
Therapy via messaging, phone, or live video chat
-
Flexible cancellation at any time
$100 off your first month with code SPACE
Please know that there’s no quick cure, however, it can be managed. There are various treatment options available to treat anorexia and bulimia. The overall goal of getting help must be:
- Detecting the underlying cause of the behavior
- Improving your relationship and self-esteem
- Changing the unhealthy or toxic patterns or behaviors
Based on the diagnosis and severity of the symptoms, your therapist is more likely to suggest:
- Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT)
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
- Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT)
- Family Therapy
- Interpersonal Psychotherapy
Related Read: Alternative Treatments for Eating Disorders
I hope this blog helps you understand the differences between anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa. Comment down and share your queries related to eating disorders.
For more such content, connect with us through all social media platforms.
Thanks for reading!